In the realm of industrial, construction and infrastructure development, the importance of plants, equipment and structures running optimally cannot be overstated. One crucial aspect of achieving this goal is the proper use of construction materials, and an often overlooked component of this is the vital role that non-shrink grouts play. According to the American Concrete Institute “a true non-shrink grout will completely and permanently fill a space.” Non-shrink grouts are essential to ensure the stability and longevity of plant and equipment. A true non-shrink grout will not exhibit shrinkage in either the plastic, or hardened stage of the curing process and will support the plant, or equipment being grouted for the life of that plant, or equipment. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of non-shrink cementitious grouts.
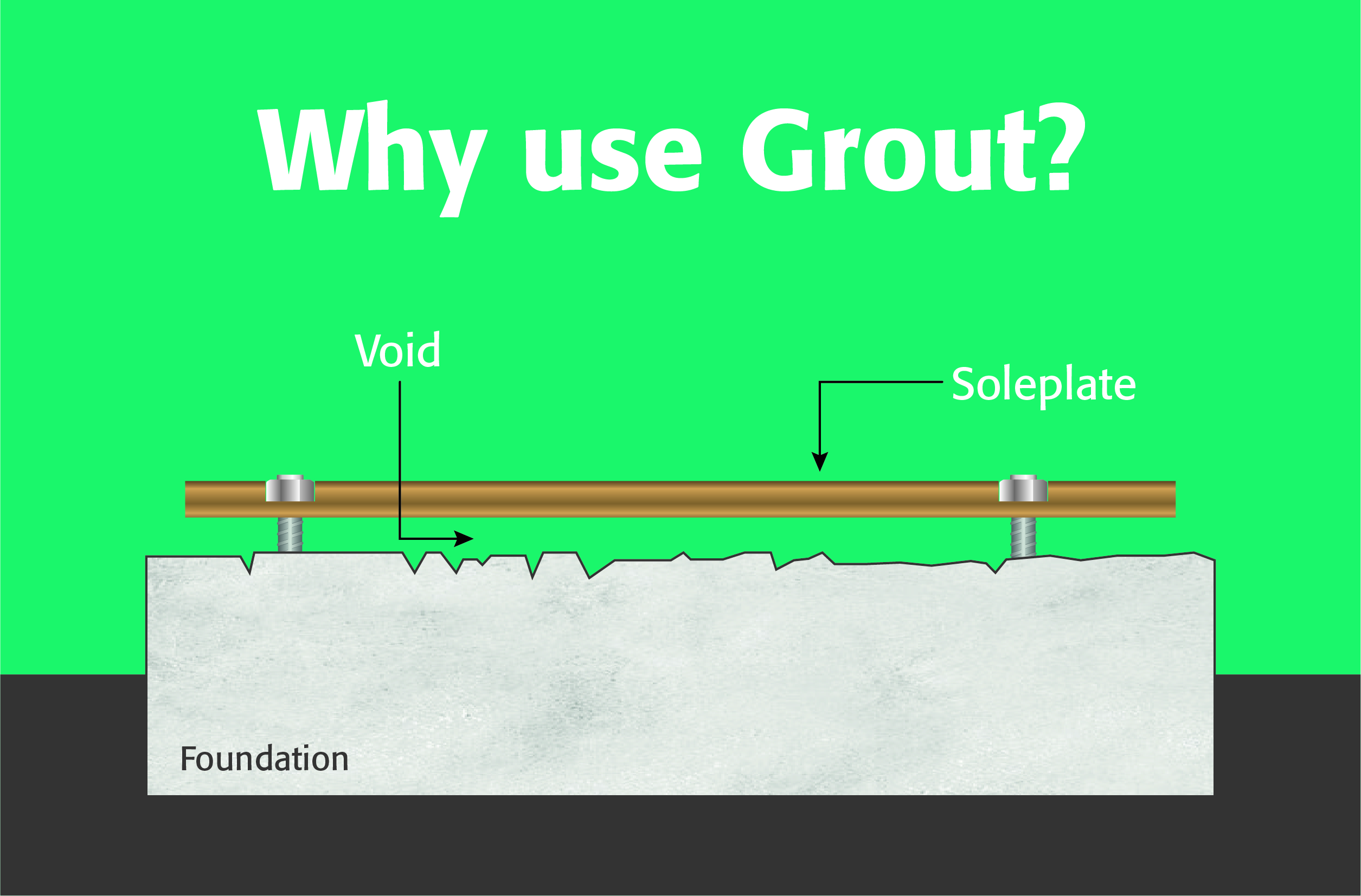
Non-shrink Cementitious Grouts are specialised construction materials used to fill voids, gaps, and spaces under various plant, equipment, columns and structures, providing structural support and dimensional stability. They are composed of a mixture of hydraulic cement, fine aggregates, and additives that help prevent the grout from shrinking in either the plastic, or hardened state. The unique formulation of non-shrink grouts makes them ideal for applications where dimensional stability is crucial and there is a Cementitious Grout available to suite every application.
Vertical Height Change and Dimensional Stability: One of the primary benefits of non-shrink cementitious grouts is their ability to maintain their original volume as they cure. This feature ensures that the grout effectively fills voids and gaps under plant & equipment without creating stresses or compromising the structural integrity of the surrounding elements. The single most important requirement of a grout is that it does not shrink and this property should be the starting requirement of any grouting specification.
Load Transfer: Non-shrink cementitious grouts are designed for static and / or light dynamic loading. They are also preferable to epoxy grouts in high service temperature applications. Non-shrink cementitious grouts offer excellent load transfer capabilities and can effectively transfer loads between structural components, minimizing alignment issues, differential movements that could lead to cracks or other issues and costly down time to re-grout equipment that has failed though misalignment.
Compressive Strength: Non-shrink cementitious grouts are engineered to provide high compressive and bond strengths. Compressive Strength requirements will vary between projects. This makes selection of the correct grout for a particular application an important consideration. Although a very important performance property, specifiers should be cautioned not to use Compressive Strength as the sole factor when specifying one grout over another. NB: If a grout shrinks, it doesn’t matter how strong it gets, it isn’t doing its job!
Durability: The composition of nonshrink grouts can include additives that enhance their durability and resistance to various environmental factors, such as freeze-thaw cycles, chemical exposure, and erosion. There are many factors to consider in determining how durable a cementitious grout will be in a particular application, these include, but are not limited to Service Temperature, whether the area is in a dry industrial plant, or in a wet water / wastewater facility. In short by considering factors that may affect durability we are ensuring the long-term performance of the grout and preventing costly down time to re-grout plant and equipment that has failed due to the grout deteriorating.
Versatility: Non-shrink grouts can be used in a wide range of applications, from grouting equipment base plates and machinery foundations to repairing concrete structures and filling voids in precast elements or grouting underwater in marine environments. There is a non-shrink cementitious grout for every application. Consistency and flowability may be important considerations when grouting tight clearances or conversely, doing large monolithic foundation re-builds and re-grouts. Working time will be important when large base plates are to be grouted, or in regions where environmental conditions may require extended working times.
Quality: When specifying a Non-shrink Cementitious Grout, it is important that clients and engineers take note of the Test Methods used for each of the published performance properties. Manufacturers should always publish the test methods that they are testing to. They should be able to provide QA / QC records for each batch of grout supplied and also current independent test data for a particular product to substantiate the results they are publishing. This ensures consistent performance of the grout used and becomes important when QA / QC test requirements are written into Inspection and Test Plans on major contracts where large quantities of grout are to be place and where performance is critical.
Base Plate Grouting: Non-shrink cementitious grouts are often used to provide support and stability to machine bases, columns, and structural elements subject to static, or light dynamic loading by filling voids underneath them and maintaining precision alignment. This prevents differential settlement and ensures uniform load distribution for the life of the plant / equipment.
Anchoring Bolts and Dowels: Non-shrink cementitious grouts are widely used for anchoring bolts, dowels, and other connectors in concrete structures. Their high strength, consistency and non-shrink properties ensure a reliable bond between the anchor and the surrounding concrete. Important consideration should always be given by the design engineer to the hole diameter to bar diameter and embedment depth of the anchors to ensure optimum performance. The anchor should always be embedded deeply enough to ensure that it will fail before the bond of the grout to the substrate does!
Precast Concrete: In the precast concrete industry, nonshrink grouts are used to fill voids between precast elements and structural members, creating a strong and monolithic connection.
Underpinning: When renovating or retrofitting structures, nonshrink grouts can be used for underpinning existing foundations to increase load-bearing capacity or correct settling issues. A Structural Engineer should always be engaged to define the scope of work correctly and to determine the required performance properties of the grout being used.
Structural Repairs: Non-shrink grouts are on occasion used for repairing damaged or deteriorated concrete structures and / or for monolithic foundation re-builds under plant and equipment. They can be used to fill voids, cracks, and damaged areas, restoring the structural integrity of the elements but special care needs to be taken regarding the methodology to be used. Remember that a true non-shrink grout wants to be restrained. Where it isn’t, the chance of differential movement & subsequent cracking increases. For large scale concrete repairs proprietary concrete repair mortar/s should be considered.
Non-shrink cementitious grouts are unsung heroes in the world where precision alignment of plant, equipment and structures is critical to their optimum performance. Their unique composition and properties make them invaluable for applications where dimensional stability and load transfer are paramount. Whether used in base plate grouting, precast connections, anchoring, or underpinning, non-shrink grouts support safe, enduring, and reliable plant, equipment and structures that stand the test of time. As technology and construction methods continue to evolve, these grouts remain a cornerstone of modern construction practices.
Find out more about our range of Euclid Chemical industrial grouting solutions or contact our National BDM Grouts & Repairs, Simon Ross to discuss your specific project requirements.
 Concrete & Masonry, Hot Topics
All you need to know about concrete curing compounds!
Concrete & Masonry, Hot Topics
All you need to know about concrete curing compounds!
Not all curing compounds are created equally, so our team has put together this handy post to help you understand all you need to know about curing compounds...

© 2025 Tremco Incorporated

